Tuesday, August 4, 2020
Graph Representation
Graph Declaration
First let us look at the components of graph data structure. To
represent graphs, we need the number of vertices, the number of edges
and also their interconnections.
Adjacency Matrix
The adjacency matrix of a graph is a square matrix of size
N × N, where N is the number of Nodes of the graph.
It is basically a Boolean matrix which is initialized with zero. Let’s
Say our adjacency matrix as Adj[][]. So Adj[u][v] is set
to 1 if there is an edge between node u and v, otherwise it is zero.
Now if the graph is undirected you can either set Adj[v][u] = 1, whenever you set Adj[u][v] = 1 or you can just leave Adj[v][u] = 0. In both the cases to save time we will just process Diagonally half of this Matrix.
Now if the graph is directed you have to consider Adj[v][u] whenever you set Adj[u][v] to 1, because Adj[v][u] ≠ Adj[u][v] for directed graph. But in that case also we will just process diagonal half of the matrix as in each step when Adj[u][v] comes we will also check Adj[v][u].
The Adjacency matrix representation is good if the graphs are dense.
The matrix requires
O(N2)
bits of Storage and
O(N2)
time for Initialization. If the number of edges is proportional to
N2,then there is no problem because
N2steps are required to read the edges.
But the Downside is that it doesn’t matter the edges are minimum or maximum it will always take same amount of Space and Time. Which is why Nowadays we don’t use this kind of implementation. If N ≤ 104, we can use It, but if N ˃ 104 We can’t use this implementation in competitive coding platforms. It will give TLE error.
Adjacency List
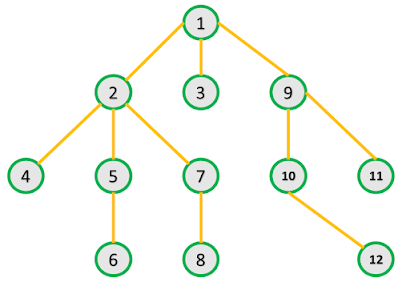
Adjacency list is better implementation. The basic concept is that we create a list of node and each list node have only those nodes which are connected to the list node.
See below Images to get better idea.
One thing to be kept in mind is that the order of edges in input is important. This is because the order in which edges appear on the adjacency list affects the order in which they are processed by algorithms.
The adjacency List takes O(N+M) of space where N is number of node and M are number of edges. Which is far more less than Adjacency matrix. Also graph traversals are fast & easier in Adjacency List.
Go to the Implementation Part to Know how They are Implemented.
More Topics will be Added Soon 💚
Monday, August 3, 2020
BASIC GRAPH THEORY
BASIC GRAPH THEORY
Introduction
In the real world many problems are represented in terms of objects and
connections between them. For example, in Railway route map we might be
interested in questions like:
“What is the fastest way to go from Lucknow to Delhi?”
To answer these questions, we use Graph Data structures.
A graph is simply a way of encoding pairwise relationships among a set of
objects. It consists of a collection of V nodes and E edges. Edge
simply connects two of the nodes but not necessarily. An edge can also go
start and end on same node, these types of edges are called self-loops. We
will discuss them on later posts.
Types of Edges
· Directed Edge
- Ordered Pair of Vertices (u, v).
- First Vertex is Origin
- Second Vertex is Destination
- Its like one-way road
· Undirected Edge
- Unordered pair of vertices (u, v).
- Its like two-way road.
Types of Graphs
-
Directed Graph
- All edges are Directed
- It is like Route Network
-
Undirected Graph
- All Edges are Undirected
- Its like Flight network
Important Points You Should Know
- A degree of vertex is the number of edges incident on it.
- Two edges are parallel if they connect the same pair of vertices.
- A graph with no cycles is called a Tree. A Tree is an acyclic connected graph.
- A self-loop is an edge that connects a vertex to itself.
- Graphs with relatively few edges are called Sparse Graphs.
- A graph is connected if there is a path from every vertex to every other vertex.
- If graph is not connected, then is consists of a set of Connected Components.
- Graphs with all edges present are called Complete graphs.
- Weighted graphs have weights assigned to each edge or node.
Graphs & Algorithms
GRAPH
1) Basic Graph Theory
i) Introduction
ii) Representation
2) Graph Implementation
ii) Adjacency List
3) Graph Algorithms
4) Graph Traversal
5) Famous Problems on Graph
More topics will be made available soon💚
Thursday, April 16, 2020
WHAT IS COMPETITIVE PROGRAMMING ?
- What is Competitive programming
- How to practice Competitive Programming
WHAT IS COMPETITIVE PROGRAMMING ?
Choose a Programming Language
Firstly, you need to select a programming language with which your are most comfortable and then learn its syntax and rules. It can be any language C, C++, C++14, Java, Python, Python 3, Ruby etc. C, C++ and Java are faster programming languages with C being the fastest among all other available languages moreover they are allowed in almost every competition or interviews. So it’s good if you choose one out of these three still there is no restriction if you are comfortable with any other language.
Understanding Time and Space Complexity
In most of the cases there is more than one solution that exists to a problem so you need to come up with the best solution as we seen earlier in the post. So it’s really important to learn about these two concepts to write an optimal solution for the problem.
Learning Data Structures and Algorithms
DSA is the heart of programming and you can not ignore it while solving coding problems in competitive programming. Array, Linked List, Stack, Queue, Tree, Trie, Graph, Sorting, Recursion, Dynamic Programming all these basic building blocks of DSA will help you to become a good programmer. The most important thing you need to know where , what and when to apply them. It means which data structure is suitable for what type of problem to get the optimal solution. Practicing questions based on DSA will you in that.
Solve Coding Problems
Now you have cleared the beginner round and now its time to practice. You need to take part in coding challenges on different coding platforms. Before participating in contest it would be great if you practice for some challenges on your own and then participate there.
Start from the basic level and once you build the confidence, get out of your comfort zone and gradually try to solve the complex problems. Below are some points you need to keep in mind once you start solving problems.
- You need to understand the input, output and test cases on online coding platforms. Check the link Solving Problem on Codechef to get started on this platform.
- The online coding platforms run your code on a lot of inputs then take out the output and store it in one place. They also have the tester's code or author's code which is one of the correct code for the problem. They run the same set of input on correct code and create the outputs and after that, they match these two outputs. If these two outputs match then your solution is considered correct.
- You may freeze out in the beginning once you see the problems on these coding platforms and think that you are not made for it or your thinking ability is not much higher to solve these questions. The reason is as a beginner you just know the syntax of the language and some basic loops or function, so when you encounter these challenges you freeze out and start doubting on your capabilities which you should not do that. You need to understand that there is a process to learn competitive programming and you have to move gradually from level 0 to the top level 💪.
Practice and Do it Regularly
Your patience, dedication, and consistency are very important to become a good competitive programmer. Keep practicing the coding questions every single day on the online coding platforms or you can also take the help of whiteboard to solve coding questions but the important thing is to do it regularly. Do not make a mistake to take a break from it once you have started. Stick on it, no matter how difficult the problem is or how much time you take to solve a single coding problem. Participate in different coding competitions and learn from other programmers. As a beginner try to practice 100 different problems rather than solving 1000 same problems, because in your early stages you need to expand your critical thinking and problem solving skill. Your daily practice makes you a perfect coder, good problem solver and you will be able to find a suitable data structure for a specific problem and that matters a lot in software development.
Never Give Up!
Never say Never because limits like fears are often an illusion - Micheal Jordan
- Hacker-earth - Indian Platform
- Codechef - Indian Platform
- Codeforces - Russian Platform
- URI
- SPOJ
- Hacker-rank - Indian-American Platform
- Top-coder - American Platform
- At-coder - Japanese Platform
- Geeksforgeeks - Indian Platform